Gentocin Injectable Solution (100 mg/mL) (Canada)
This treatment applies to the following species: Company: Merck Animal Health
Company: Merck Animal Health
Gentamicin Injection
(as gentamicin sulfate 100 mg/mL)
Sterile Antibiotic
DIN 00592293
VETERINARY USE ONLY
FOR INTRAMUSCULAR ADMINISTRATION TO: DOGS, CATS, AND PIGLETS.
FOR INTRA-UTERINE ADMINISTRATION TO HORSES, DOGS, AND COWS.
FOR SUBCUTANEOUS ADMINISTRATION TO DOGS, CATS, TURKEY POULTS, AND CHICKS.
Structural Formula And Chemistry
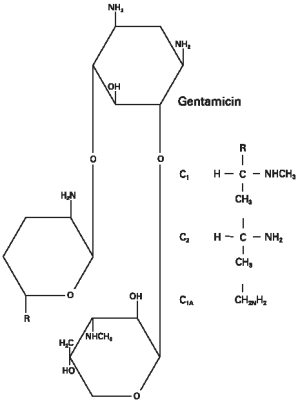
Description
GENTOCIN injectable solution, gentamicin as sulfate, is a water soluble (bactericidal) antibiotic of the aminoglycoside group, derived from Micromonospora purpurea, an actinomycete. GENTOCIN injectable solution 100 mg/mL is a sterile aqueous solution. Ingredients: each mL contains: Medicinal Ingredient: gentamicin (as sulfate) 100 mg; Non-Medicinal Ingredients: 10 mg benzyl alcohol as preservative, 2.4 mg sodium metabisulfite, 0.8 mg sodium sulfite anhydrous, and 0.1 mg edetate disodium.
Gentocin Injectable Solution (100 mg/mL) Indications
GENTOCIN injectable solution is clinically effective in infections due to susceptible gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, indole negative and indole positive Proteus species, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter aerogenes, Arizona hinshawii, and Staphylococcus species. The use of GENTOCIN injectable solution is indicated in the treatment of infections caused by laboratory determined susceptible bacteria, with due regard for relative antibiotic toxicity. Therefore, the drug should be considered as follows:
|
Indication |
Route |
Species |
|
1) Urinary tract infections (cystitis and nephritis) |
I.M./S.C. |
Dogs and Cats |
|
2) Bacteremia/Septicaemia |
I.M./S.C. |
Dogs and Cats |
|
3) Infected wounds |
I.M./S.C. |
Dogs and Cats |
|
4) Soft tissue infections |
I.M./S.C. |
Dogs and Cats |
|
5) Respiratory tract infections |
I.M./S.C. |
Dogs and Cats |
|
6) Gastrointestinal tract infections |
I.M./S.C. |
Dogs and Cats |
|
7) Scours (E. coli) |
I.M. |
1-3 day old piglets |
|
8) Uterine infections |
||
|
i. Bacterial infections of the uterus (metritis) |
I.U./I.M. |
Dogs |
|
ii. Bacterial infections of the uterus (metritis) |
I.U. |
Horses |
|
iii. Metritis and cervicitis associated with bacteria such as E. coli, S. aureus and Streptococcus species which are susceptible to gentamicin. |
I.U. |
Cows |
|
The method of treatment of metritis associated with systemic involvement should be at the discretion of the attending veterinarian. |
||
|
9) As an aid in the prevention of mortality in the first two weeks of life of 1 to 3 day old turkey poults due to Arizona hinshawii infections |
S.C. |
|
|
10) Prevention of early mortality caused by Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, susceptible to gentamicin. |
S.C. |
One day old chicks |
In the majority of cases bacteriologic cultures should be obtained initially, to identify the causative organism and to determine its sensitivity to GENTOCIN injectable solution. Sensitivity discs of 10 µg are available for this purpose.
GENTOCIN injectable solution should also be considered in Staphylococcal infections when other conventional anti-microbial therapy is inappropriate or when bacterial susceptibility testing and clinical judgment indicate its use.
If susceptibility tests indicate the causative organism is resistant to gentamicin, other antimicrobial therapy should be instituted.
Gentocin Injectable Solution (100 mg/mL) Dosage And Administration:
INTRA-UTERINE:
(a) Horses: 2.0 - 2.5 grams once per day for three to five days during estrus. Each dose should be diluted with 200-500 mL sterile physiological saline before aseptic uterine infusion.
Although GENTOCIN injectable solution is not spermicidal, treatment should not be given the day of breeding.
(b) Dogs: 4.4 mg/kg (2 mg/lb) body weight once a day for four days. Each dose should be diluted with 10 mL sterile physiological saline before aseptic uterine infusion.
(c) Cows: 200 mg one time only. The dose should be diluted with 16 mL sterile physiological saline solution before aseptic uterine infusion. Although GENTOCIN injectable solution is not spermicidal, treatment should not be given the day of breeding.
INTRAMUSCULAR:
(a) Dogs and Cats: 4.4 mg/kg (2 mg/lb) body weight twice the first day: 4.4 mg/kg (2 mg/lb) body weight once a day thereafter. Average duration of treatment in clinical studies was five to seven days.
Ordinarily, treatment should not be given for more than 7 to 10 days or be repeated unless required for serious infections not responsive to other agents. The decision to continue therapy with GENTOCIN injectable solution should be based on results of the sensitivity tests, clinical response of the patient, and consideration of relative antibiotic toxicity. Results of in vivo and in vitro studies indicate that alkalinization of the urine may be a useful therapeutic adjunct. In clinical studies, a small percentage of animals experienced pain on administration.
(b) Piglets: Each 1-3 day old piglet should be injected aseptically once intramuscularly with 5 mg of GENTOCIN injectable solution. To prepare 50 mL of 5 mg/mL solution, dilute 2.5 mL of GENTOCIN injectable solution 100 mg/mL with 47.5 mL of sterile physiological saline solution. Inject 1 mL per piglet.
SUBCUTANEOUS:
(a) Dogs and Cats: 4.4 mg/kg (2 mg/lb) body weight twice the first day: 4.4 mg/kg (2 mg/lb) body weight once a day thereafter. Average duration of treatment in clinical studies was five to seven days.
(b) Turkey Poults: Each turkey poult should be injected aseptically once subcutaneously in the neck with 1 mg of GENTOCIN injectable solution. To prepare 50 mL of 5 mg/mL solution, dilute 2.5 mL of GENTOCIN injectable solution 100 mg/mL with 47.5 mL of sterile physiological saline solution. Inject 0.2 mL per turkey poult.
(c) Chicks: Each one-day old chick should be injected aseptically once subcutaneously in the neck with GENTOCIN injectable solution diluted with sterile physiological saline solution to provide 0.2 mg gentamicin in a 0.2 mL dose. This concentration can be provided by diluting GENTOCIN injectable solution as follows.
GENTOCIN - injectable solution
|
100 mg/mL (mL) |
Sterile Saline (mL) |
No. Doses |
Dose/Chick (mL) |
|
0.5 |
49.5 |
250 |
0.2 |
|
1.0 |
99.0 |
500 |
0.2 |
|
2.0 |
198.0 |
1,000 |
0.2 |
|
5.0 |
495.0 |
2,500 |
0.2 |
|
25.0 |
2,475.0 |
12,500 |
0.2 |
Ordinarily, treatment should not be given for more than 7 to 10 days or be repeated unless required for serious infections not responsive to other agents. The decision to continue therapy with GENTOCIN injectable solution should be based on results of the sensitivity tests, clinical response of the patient, and consideration of relative antibiotic toxicity.
Results of in vivo and in vitro studies indicate that alkalinization of the urine may be a useful therapeutic adjunct.
In clinical studies, a small percentage of animals experienced pain on administration.
CONTRA-INDICATIONS: A history of hypersensitivity or toxic reactions to gentamicin are contraindications to its use.
CAUTIONS: Do not premix with other drugs. Pregnancy: Although studies in pregnant animals have not revealed teratogenic effects, caution should be exercised.
Ototoxicity: Gentamicin, in common with the antibiotics streptomycin, neomycin, and kanamycin, has produced ototoxicity in experimental animals and man. This adverse reaction which may be delayed in onset, is manifested primarily by damage to vestibular function. The reversibility of this adverse reaction is frequently contingent upon early recognition of potential ototoxicity. Complete damage has occurred mainly in humans who were uremic, had renal dysfunction, had prior therapy with ototoxic drugs, or received higher doses and longer courses of therapy than those recommended. In animals who have previously been treated with drugs likely to affect eighth cranial nerve function (e.g., streptomycin, neomycin, kanamycin, etc.) GENTOCIN injectable solution should be used with caution and with the understanding that toxic effects may be cumulative with these agents.
Nephrotoxicity: Nephrotoxicity, manifested by an elevated blood urea nitrogen or serum creatinine level or a decrease in the creatinine clearance may occur with GENTOCIN injectable solution. In most cases, these changes have been reversible when the drug has been discontinued. The administration of other potentially nephrotoxic agents prior to or in conjunction with GENTOCIN injectable solution may increase the risk of nephrotoxicity.
In animals with suspected or impaired renal function, daily serum determinations for GENTOCIN injectable solution should be carried out to avoid excessive and potentially toxic serum levels of GENTOCIN injectable solution.
Neuromuscular Blocking Action: Neuromuscular blockage and respiratory paralysis have been reported in the cat receiving high doses (40 mg/kg) of gentamicin. The possibility of these phenomena occurring should be considered if gentamicin is administered to animals receiving general anesthesia and/or neuromuscular blocking agents such as succinylcholine or tubocurarine. Neuromuscular blocking action by gentamicin in animals may be antagonized by neostigmine or calcium.
Superinfections: As with other antibiotics, treatment with gentamicin may occasionally result in overgrowth of non-sensitive organisms. If superinfection occurs, appropriate measures should be taken.
Warnings
Treated animals must not be slaughtered for use in food for at least: 30 days (Cows); 42 days (Piglets); 63 days (Turkey Poults); and 35 days (Chickens) after the latest treatment with this drug.
Do not use in lactating dairy cows.
Do not use in calves to be processed for veal.
Do not use in laying birds.
Do not use in horses that are to be slaughtered for use in food.
This product should be handled carefully to avoid accidental self-injection.
In case of accidental self-injection, seek medical advice and show the package insert to the physician.
Keep out of reach of children.
Clinical Pharmacology
When gentamicin is administered intramuscularly, peak serum concentrations, bactericidal for susceptible bacteria, occur between 30 and 90 minutes after injection: effective concentrations persist for six to eight hours.Minimal amounts of gentamicin are absorbed following oral administration. Therefore oral administration is not recommended for treatment of systemic infections. About 25-30% of the administered dose of gentamicin is bound by serum protein: it is released as the drug is excreted.
GENTOCIN is excreted principally in the urine by glomerular filtration.
After initial administration to humans with normal renal function, 30-100% of the gentamicin is recoverable in the urine in 24 hours. Renal clearance of Gentocin is similar to that of endogenous creatinine.
Gentamicin has been found in the cerebrospinal fluid after intramuscular injection: however, concentrations have been low and may be inadequate for treatment of certain central nervous system infections.
Gentamicin has also been found in the sputum, pleural fluid and peritoneal cavity. Gentamicin crosses the peritoneal as well as the placental membrane.
GENTOCIN injectable solution at considerably higher doses than normally recommended, like other aminoglycoside antibiotics, causes neuromuscular blockage in animals. This phenomenon is antagonized by neostigmine or calcium (See CAUTIONS).
MICROBIOLOGY: GENTOCIN injectable solution is a bactericidal antibiotic which affects bacterial growth by specific inhibition of normal protein synthesis in susceptible bacteria. It is active against a wide variety of pathogenic gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus species (both indole positive and indole negative), Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter aerogenes, and Staphylococcus species (including penicillin and methicillin-resistant strains).
In addition, gentamicin sulfate is active in vitro against species of Salmonella, Shigella, Serratia marcescens and Neisseria; certain species of Streptococcus including some strains which are sensitive to gentamicin. Only minimal activity has been found against Streptococcus faecalis and Diplococcus pneumoniae. Limited data suggest sensitivity of some strains of Mycoplasma.
Most anaerobes (Species of Clostridium, Bacteroides, and Diphteroids) are resistant. The bactericidal concentration of gentamicin is usually one to four times the minimal inhibitory concentration. Gentamicin was over eight times more active in vitro at pH 7.5 than at pH 5.5, against several common urinary pathogens.
Gentamicin is excreted in an unchanged form, mainly by glomerular filtration. This results in high urinary concentrations of the antibiotic.
Clinical studies have shown that organisms previously sensitive to gentamicin have become resistant during therapy. Although this has occurred infrequently, the possibility should nevertheless be considered. There is evidence that cross resistance between gentamicin and the aminoglycoside antibiotics may occur since bacteria made resistant to aminoglycoside antibiotics artificially in the laboratory are also resistant to gentamicin; however, GENTOCIN injectable solution may be active against clinical isolates of bacteria resistant to other aminoglycosides. Conversely, organisms resistant to GENTOCIN injectable solution may be sensitive to other aminoglycoside antibiotics.
TOXICOLOGY: GENTOCIN injectable solution has been shown to affect vestibular and renal functions in animals and man. Chronic administration of 5 mg/kg for 50 days in dogs, 10 mg/kg for 40 days in cats and 20 mg/kg for 24 days in rats resulted in mild toxicity in some animals studied. Higher toxic doses resulted in renal and vestibular function damage which appeared to be dose related. In humans the only serious side effect to date has been damage to the eighth cranial nerve predominantly the vestibular branch. Proteinuria, a rise in blood urea nitrogen or serum creatinine have also occurred. These findings have usually reverted to normal when the drug was discontinued.
No toxicity was observed in neonatal pigs injected with gentamicin at three times the recommended dose for twice the recommended treatment period. No adverse effects were reported during clinical studies in piglets up to three days of age.
During clinical evaluation no visible signs of toxicity were noted with GENTOCIN injectable solution doses as high as 10 mg per poult subcutaneously. The LD50 for day old turkey poults is calculated to be 27.8 mg per male poult and 40.5 mg per female poult.
Storage
Store between 2° and 25°C. Protect from freezing.How Supplied
GENTOCIN injectable solution 100 mg/mL is packaged in 100 mL multiple dose vials containing 100 mg/mL of gentamicin base in an aqueous solution of a pH of 4.5 for parenteral administration.REFERENCES
1. Weinstein, M.J. & al. Gentamicin, a new broad spectrum antibiotic complex. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 1963, p. 1-7.
2. Black, J. & al. Pharmacology of gentamicin a new broad spectrum antibiotic. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy- 1963, p. 138-147.
3. Finland, M. Gentamicin: Antibacterial activity. clinical pharmacology, and clinical applications. Medical Times 97:161-74.
4. Cox, C.E. Gentamicin, Medical Clinics of North America 54:1305-1315.
5. Sager, F.C. Management and medical treatment of uterine disease. J.A.V.M.A. 153 1567-1569.
6. Peterson, FB. & al. Studies on the pathogenesis of endometritis in the mare. Proc. 15th Ann. Conv. A.A. of E.P. Dec. 69. p. 279-282.
7. Hughes, J.F. & al. The occurrence of Pseudomonas in the reproductive tract of mares and its effect on fertility. The Cornell Veterinarian. Vol. LVI, No. 4, Oct. 66, p. 595-610.
8. Berkman, RH. et al. Gentamicin new broad spectrum antibiotic for treatment of canine urinary tract infections. Schering Corporation. Animal Health Research Centre, Feb. 71.
INTERVET CANADA CORP., KIRKLAND, QUÉBEC, H9H 4M7
1 866 683-7838
Last revision: April 1st, 2021
Intervet Canada Corp. is a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc.
® Intervet Canada Corp.
CPN: 1208051.6
Intervet Canada Corp.
16750 ROUTE TRANSCANADIENNE, KIRKLAND, QC, H9H 4M7
| Order Desk: | 514-428-7013 | |
| Toll-Free: | 866-683-7838 | |
| Fax: | Toll-free 888-498-4444; local 514-428-7014 | |
| Website: | www.merck-animal-health.ca |
 |
THIS SERVICE AND DATA ARE PROVIDED "AS IS". Animalytix assumes no liability, and each user assumes full risk, responsibility, and liability, related to its use of the Animalytix service and data. See the Terms of Use for further details. |

Copyright © 2024 Animalytix LLC. Updated: 2024-02-27
