Testicular Torsion
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
What is testicular torsion?
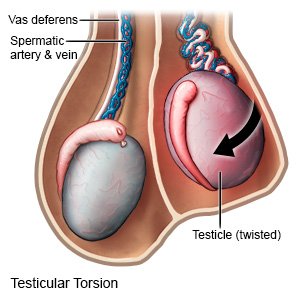
Testicular torsion is a condition that causes the testicle to be twisted with the spermatic cord. A spermatic cord holds each testicle. The cord contains blood vessels and passageways for sperm. When the spermatic cord is twisted, blood flow to the testicle is reduced or blocked. The lack of blood flow can cause testicle necrosis (tissue death). Testicular torsion needs immediate care to prevent this from happening. This condition usually happens to only one testicle but can happen to both.
 |
What causes or increases my risk for testicular torsion?
The cause of this condition is not always known. Testicular torsion usually affects babies up to 1 year of age and children 12 to 18 years of age. It can also happen to adults. Any of the following may increase your risk:
- A birth defect
- Sports or exercise
- An injury near the groin
- Cold weather
What are the signs and symptoms of testicular torsion?
- Severe pain and tenderness in your scrotum
- Red and swollen scrotum
- Testicles that appear to hang a bit higher than usual
- Nausea and vomiting
How is testicular torsion diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you and ask about your symptoms. Include when the symptoms began and how severe they are. Any of the following may be used to check for testicular torsion:
- An ultrasound uses sound waves to show pictures on a monitor. An ultrasound may show problems in your testicles and spermatic cord, including abnormal blood flow.
- Scintigraphy uses radioactive dye to check for blood flow in the spermatic cord and scrotum. The dye helps the blood vessels show up better on the x-rays.
- Surgery may be needed so healthcare providers can see your testicle to check for torsion.
How is testicular torsion treated?
You must see a healthcare provider as soon as possible. You may need any of the following:
- Medicine may be given to relieve any pain or swelling.
- Reduction means your provider tries to untwist the spermatic cord by hand. You will need surgery later, even if reduction works.
- Surgery may be used to untwist the spermatic cord. Your surgeon will make an incision on your scrotum to reach and untwist the affected testicle. Your surgeon will also check to see if a lack of blood flow damaged the testicle. The testicle may need to be removed. If it does not need to be removed, it will be attached to the wall of your scrotum to prevent another torsion. The other testicle will also be attached to prevent torsion.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have increased pain, swelling, or redness in your scrotum.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever.
- Your skin is itchy, swollen, or has a rash.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
