Penis Fracture
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
What do I need to know about a penis fracture?
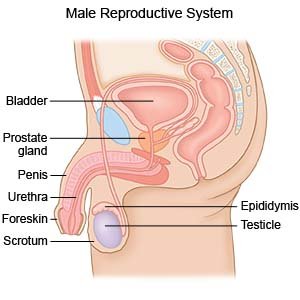
A penis fracture happens when an erect penis is injured. The penis has 2 chambers that fill with blood to cause an erection. A fracture happens when the chambers are filled with blood and the penis is bent suddenly or with too much force. The bend ruptures the outer lining of one chamber, called the tunica albuginea. A penis fracture usually happens during sex. It can also happen if you fall or roll onto your erect penis or hit it on something. It is important to seek immediate care for this injury. Without treatment, a penis fracture can lead to permanent damage.
 |
What are the signs and symptoms of a penis fracture?
- A popping or cracking sound and then a rapid loss of the erection
- Swelling or bulging of your penis, along with skin that turns purple (called an eggplant deformity)
- Pain in or around your penis
- Bruised skin in or around your genital area
- A hematoma (collection of blood) on your penis
- A bent or abnormal penis shape
- Blood in your urine or at the tip of your penis, if your urethra was also injured
How is a penis fracture diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider may be able to see you have a penis fracture during your exam. Tell your provider about your symptoms and when they began. You may be given contrast liquid before any of the following to help the fracture show up better in pictures. Tell a healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. The following are commonly used to check for a penis fracture:
- Ultrasound pictures may show a rupture of the tunica albuginea. The pictures may also show other injuries to your penis, urethra, or nearby tissues.
- MRI pictures may be used if ultrasound pictures do not show the area clearly enough. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell a healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- A urethrogram may be used to check for an injury to your urethra, such as a tear. The urethra is a long tube that carries urine from your bladder through your penis. Semen also travels through the urethra during ejaculation.
How is a penis fracture treated?
Do not try to let your penis heal on its own. Treatment is the best way to prevent permanent problems, such as erectile dysfunction (problems having or keeping an erection). The following are commonly used to treat a penis fracture:
- Surgery is the main treatment. A surgeon will use absorbable stitches to repair the tunica albuginea. Blood that has pooled in the area will be removed. Surgery may also be used to straighten your penis. You may need surgery to fix a tear in your urethra or in blood vessels. Your healthcare provider will tell you if surgery should happen immediately or after swelling goes down.
- Medicines may be recommended to relieve or prevent pain or swelling.
What can I do to manage or prevent a penis fracture?
The following are some things you can do at home to be more comfortable and prevent more injury. You will still need treatment such as surgery to heal the injury. Talk to your healthcare provider before you try any of the following:
- Apply an ice pack to your penis, if directed. Ice helps relieve or prevent pain and swelling. Cover the pack with a towel before you apply it to your penis. Apply the ice pack for 10 to 15 minutes every hour, or as directed.
- Wrap your penis or use a splint, if directed. Your provider will tell you if this may help. The provider will tell you what to use and show you how to apply the wrap or splint. Ask how long to use the wrap or splint each day.
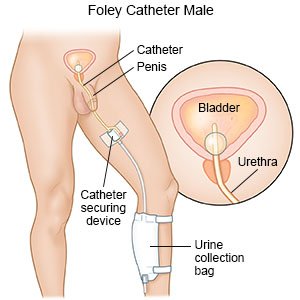
- A Foley catheter may be needed. A Foley catheter is a sterile tube that is inserted into your bladder to drain urine. The tip of the catheter has a small balloon filled with solution that holds the catheter in your bladder.
- Avoid sexual activity until your provider says it is okay. Your provider can tell you when it is safe for you to start having sex again. The provider can also tell you which sexual activities are okay for you to do.
- Be careful during any activity that can lead to a penis fracture. Do not suddenly or forcefully bend your erect penis on purpose. Try to be careful during sexual intercourse or masturbation.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You see new or more blood in your urine.
- You are not able to urinate, or you urinate very little.
- You have new or worsening pain in your penis or genital area.
- You think you fractured your penis.
When should I call my doctor or urologist?
- You have trouble getting or keeping an erection after you are told it is okay to have sex.
- You have pain that does not get better even with pain medicine.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
