Hydronephrosis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
What is hydronephrosis?
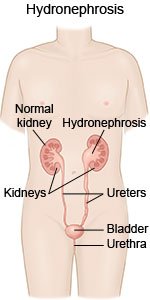
Hydronephrosis is swelling in one or both kidneys caused by urine buildup. Urine normally flows from the kidneys to the bladder through tubes called ureters. A blockage in the ureters can prevent urine from flowing properly. Urine flow may also be prevented or slowed if your kidneys do not work correctly. Urine flows back into your urinary tract. Pressure builds up in the kidney and causes swelling.
 |
What increases my risk for hydronephrosis?
- Nerve damage or narrowed blood vessels
- Kidney stones, blood clots, or tumors that cause a blockage
- Urinary tract infections
- Body changes during pregnancy
- Enlarged prostate
What are the signs and symptoms of hydronephrosis?
You may have no signs or symptoms, or you may have any of the following:
- Frequent urinary tract infections
- Mild or severe lower back pain that may spread to the groin
- Urinating little or not at all, even with an urge to urinate
- Dribbling urine, or loss of urine control
- Blood or pus in your urine
- Nausea, vomiting, fever, or chills
- Abdominal fullness or swelling
- Weight gain that you cannot explain
How is hydronephrosis diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you and ask you about your signs and symptoms. Your provider may also feel your abdomen or pelvis for any pain or swelling. You may also need any of the following:
- Blood tests show if your kidneys are working properly or have a blockage.
- Kidney function tests show how well your kidneys are working.
- X-rays may be taken of your kidneys, bladder, and ureters. You may need to have dye injected into your kidneys before the x-rays to help healthcare providers find the blockage. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast dye.
- Urine tests show how much urine your body is removing. They may also show if you have infection, blood, or protein in your urine. This may mean your kidneys are not working as they should.
- A CT scan (CAT scan) uses an x-ray and a computer to take pictures of your kidneys, bladder, and ureters. The pictures may show a kidney stone or other obstruction.
- An ultrasound may be used to show your kidney or bladder size, and if either is swollen. Ultrasound can also be used to find kidney stones. You may need to have a CT and an ultrasound together to find a blockage.
How is hydronephrosis treated?
Treatment may help keep your kidneys healthy, and prevent infection. You may need the following:
- A renal diet is a meal plan that includes foods that are low in sodium (salt), potassium, and protein. Your healthcare provider may also tell you to eat and drink more vegetables and juices.
- Stone removal may be used to remove the kidney stones that are slowing or blocking your urine flow. Your healthcare provider may use strong sound waves called shock wave therapy to break up large kidney stones. This will help make them small enough for you to pass them when you urinate.
- Catheter or stent placement may be needed to help increase your urine flow. You may need a catheter (flexible tube) placed directly into your bladder to drain urine. Your healthcare provider may place a hard plastic tube called a stent inside your urinary tract to help urine pass from your kidney to your bladder.
- Surgery may be needed to remove part or all of your kidney if it is not working properly. Your prostate may need to be removed if it is so large that it is blocking urine flow.
What are the risks of hydronephrosis?
Swelling in one or both kidneys from too much urine buildup may lead to long-term kidney damage. Partial blockages may cause loss of urine control. Severe hydronephrosis may cause a blood infection called sepsis. Sepsis is toxin (poison) buildup in your blood. It happens when your kidneys cannot flush toxins out of your body. It could also paralyze your intestines. Your kidneys could fail without treatment. These conditions may be life-threatening.
When should I contact my healthcare provider?
- Your abdomen feels full.
- You have a change in how much or how often you urinate.
- You urinate more times at night and in larger amounts than during the day.
- You have mild lower back pain or pain on one side when you urinate.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have severe, stabbing back pain.
- You have blood in your urine.
- You cannot urinate, or you urinate very little.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Hydronephrosis
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
